
Rice Science ›› 2020, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (6): 493-503.DOI: 10.1016/j.rsci.2020.09.006
• Research Paper • Previous Articles Next Articles
Ruili Li1, Jiaoling Wang2, Lei Xu3, Meihao Sun1, Keke Yi3( ), Hongyu Zhao3(
), Hongyu Zhao3( )
)
Received:2019-12-19
Accepted:2020-05-08
Online:2020-11-28
Published:2020-11-28
About author:#These authors contributed equally to this work
Ruili Li, Jiaoling Wang, Lei Xu, Meihao Sun, Keke Yi, Hongyu Zhao. Functional Analysis of Phosphate Transporter OsPHT4 Family Members in Rice[J]. Rice Science, 2020, 27(6): 493-503.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
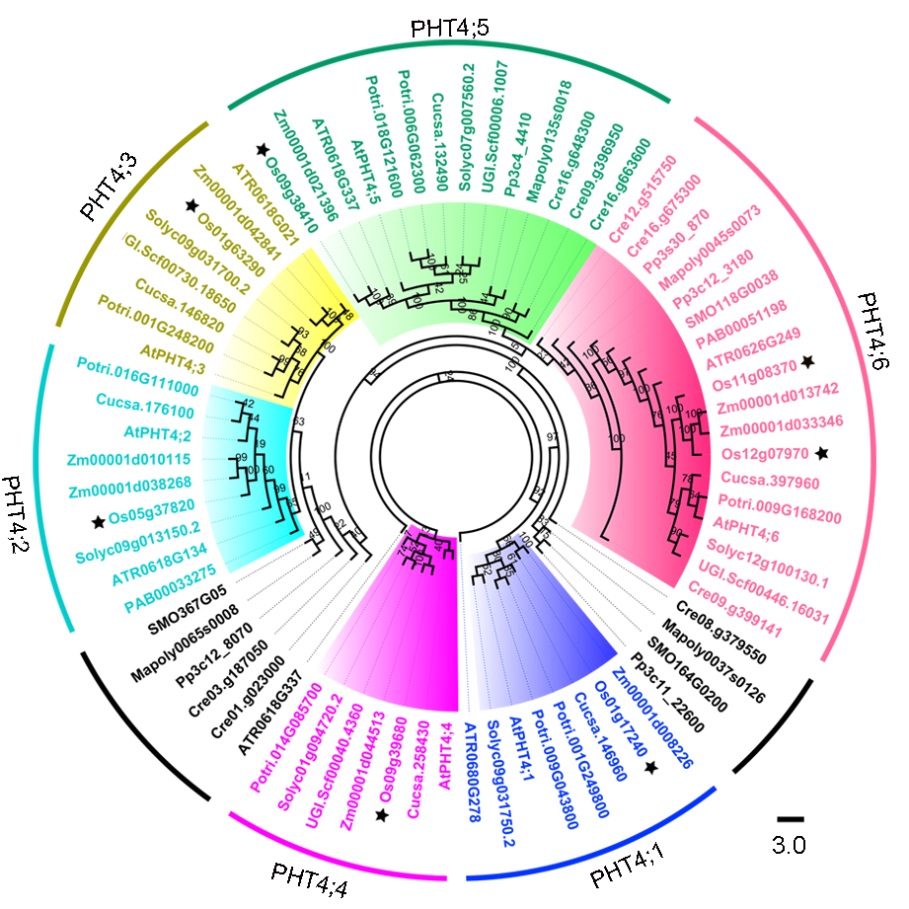
Fig. 1. Phylogenetic tree analysis of PHT4 family members.Maximum-likelihood phylogenetic analysis using PHT4 protein sequences from 12 different plant species and 1 chlorophyta. The different colours indicate different PHT4 families: blue, PHT4;1; cyan, PHT4;2; yellow, PHT4;3; purple, PHT4;4; green, PHT4;5; pink, PHT4;6; and black, Other clustering trees. Letters in the codes represent species names as follows: At, Arabidopsis thaliana; ATR, Amborella trichopoda; Cre, Chlamydomonas reinhardtii; Cucsa, Cucumis sativus; Mapoly, Marchantia polymorpha; Os, Oryza sativa; PAB, Picea abies; Potri, Populus trichocarpa; Pp, Physcomitrella patens; SMO, Selaginella moellendorffii; Solyc, Solanum lycopersicum; UGI.scf, Utricularia gibba; Zm, Zea mays.
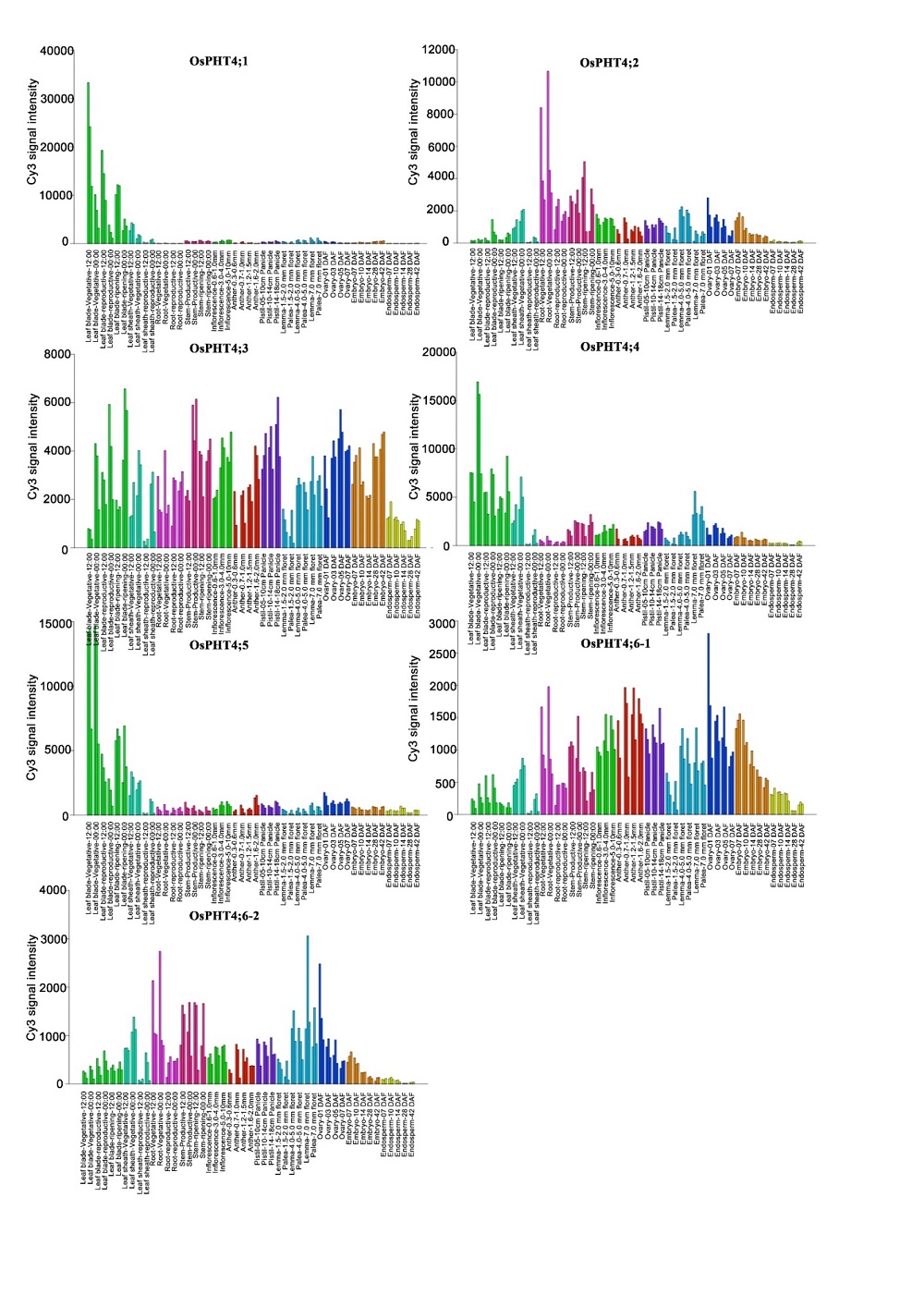
Supplemental Fig. 1. Transcript profiles of PHT4 family members in spatial temporal expression data in RiceXPro (https://ricexpro.dna.affrc.go.jp/GGEP/).
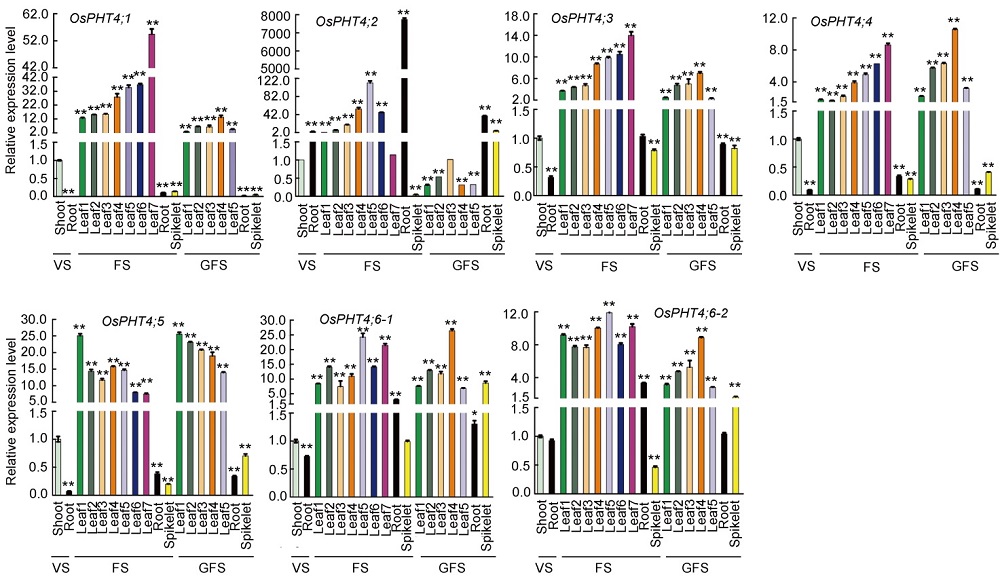
Fig. 2. Transcript profiles of PHT4 family members in various organs in rice. The expression levels of OsPHT4s were represented as relative to the respective value of shoots at the vegetative stage. VS, Vegetative stage (21-day-old plants); FS, Flowering stage (48-day-old plants); GFS, Grain filling stage (60-day-old plants). Leaf 1?7 refer to true leaves from the 1st to the 7th.Data are Mean ± SD (n = 3). *, P ≤ 0.05 and **, P ≤ 0.01 by the Student’s t-test.

Fig. 3. Subcellular localization of OsPHT4 genes in rice protoplast.Expression of p35S:OsPHT4s-GFP in rice protoplasts. The green signals indicate green fluorescent protein (GFP) and the red signals indicate autofluorescence of chlorophyll (the first six panels) and mcherry (Golgi marker) (the last two panels), respectively. In the last two panels, the GFP-OsPHT4;6-1/GFP-OsPHT4;6-2 construct and a Golgi marker were introduced into rice protoplasts for transient co-expression. BF, Bright field. Scale bars, 10 μm.
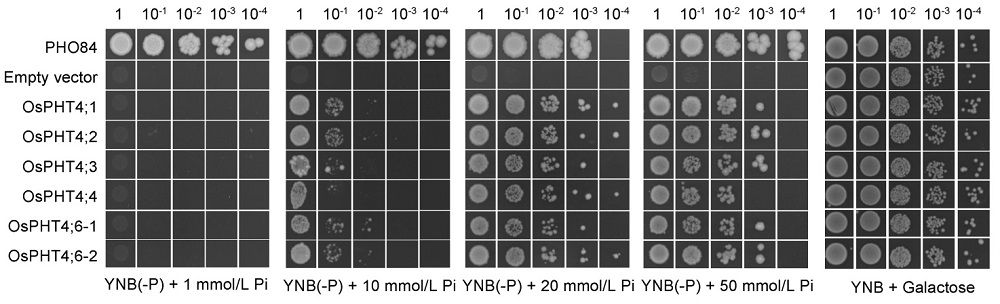
Fig. 4. OsPHT4 genes can confer Pi transport activity in yeast.Complementation of yeast mutant YP100 (Δpho84Δpho87Δpho89Δpho90Δpho91Δgit1) by the OsPHT4 genes. Equal volumes of 10-fold serial dilutions were applied to YNB(-P) (pH 5.5) medium with different Pi concentrations, and incubated at 30 ºC for 4 d. PHO84 is a high-affinity phosphate transporter and serves as a positive control, and empty vector as a negative control. YNB, Yeast nitrogen base without amino acids.

Supplemental Fig. 2. Analysis of OsPHT4 gene family promoter sequences.ABRE element, ABA responsive element, a cis-element involved in ABA response; P1BS element, PHR1 binding site, a cis-element enriched in phosphorus starvation induced gene promoters. The promoter length is 2500 bp for each gene.
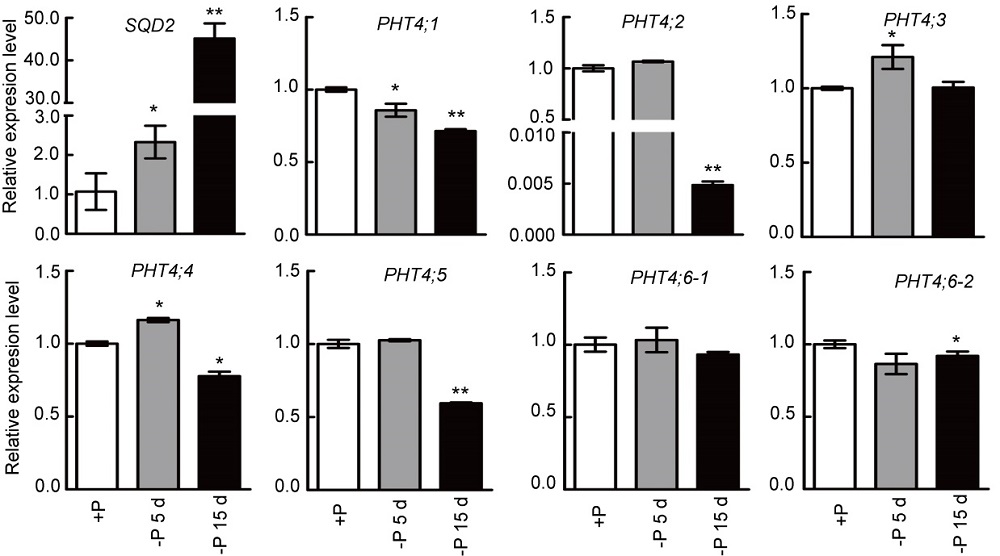
Fig. 5. Dynamic changes of transcript levels of OsPHT4 genes during phosphate deprivation in shoots of rice seedlings. The expression level was represented as relative to the value under +P conditions. The wild-type plants were grown under Pi-replete conditions (200 mmol/L) for two weeks and then transferred to Pi starvation conditions (0 mmol/L). Shoot tissues were harvested from plants exposed to Pi-limiting conditions for 5 and 15 d, and the expression levels were compared with those detected under Pi-replete conditions. SQD2 was used to control the efficiency of phosphate deprivation treatments. Data are Mean ± SD (n = 3). *, P ≤ 0.05 and **, P ≤ 0.01 by the Student’s t-test.

Fig. 6. Dynamic changes of transcript levels of OsPHT4 genes in response to abscisic acid (ABA), salt and salicylic acid (SA) stresses in roots of rice seedlings. The expression level was represented as relative to the value at 0 h. Fourteen-day-old seedlings grown under normal conditions were exposed to different chemical treatments for various time periods. ABA, 100 mmol/L; NaCl, 100 mmol/L; SA, 500 μmol/L. OsbZIP23 was used to control the efficiency of ABA and NaCl treatments. OsWRKY45 was used to control the efficiency of SA treatments.Data are Mean ± SD (n = 3). *, P ≤ 0.05 and **, P ≤ 0.01 by the Student’s t-test.
| [1] | Ai P H, Sun S B, Zhao J N, Fan X R, Xin W J, Guo Q, Yu L, Shen Q R, Wu P, Miller A J, Xu G H.2009. Two rice phosphate transporters, OsPht1;2 and OsPht1;6, have different functions and kinetic properties in uptake and translocation. Plant J, 57(5): 798-809. |
| [2] | Ayadi A, David P, Arrighi J F, Chiarenza S, Thibaud M C, Nussaume L, Marin E.2015. Reducing the genetic redundancy of Arabidopsis PHOSPHATE TRANSPORTER1 transporters to study phosphate uptake and signaling. Plant Physiol, 167(4): 1511-1526. |
| [3] | Chang M X, Gu M, Xia Y W, Dai X L, Dai C R, Zhang J, Wang S C, Qu H Y, Yamaji N, Ma J F, Xu G H.2019. OsPHT1;3 mediates uptake, translocation, and remobilization of phosphate under extremely low phosphate regimes. Plant Physiol, 179(2): 656-670. |
| [4] | Cubero B, Nakagawa Y, Jiang X Y, Miura K J, Li F, Raghothama K G, Bressan R A, Hasegawa P M, Pardo J M.2009. The phosphate transporter PHT4;6 is a determinant of salt tolerance that is localized to the Golgi apparatus of Arabidopsis. Mol Plant, 2(3): 535-552. |
| [5] | Deng M J, Hu B, Xu L, Liu Y, Wang F, Zhao H Y, Wei X J, Wang J C, Yi K K.2014. OsCYCP1;1, a PHO80 homologous protein, negatively regulates phosphate starvation signaling in the roots of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Mol Biol, 86: 655-669. |
| [6] | Guo B W, Jin Y H, Wussler C, Blancaflor E B, Motes C M, Versaw W K.2008a. Functional analysis of the Arabidopsis PHT4 family of intracellular phosphate transporters. New Phytol, 177(4): 889-898. |
| [7] | Guo B W, Irigoyen S, Fowler TB, Bersaw W K.2008b. Differential expression and phylogenetic analysis suggest specialization of plastid-localized members of the PHT4 phosphate transporter family for photosynthetic and heterotrophic tissues. Plant Signaling Behav, 3(10): 784-790. |
| [8] | Hassler S, Lemke L, Jung B, Mohlmann T, Kruger F, Schumacher K, Espen L, Martinoia E, Neuhaus H E.2012. Lack of the Golgi phosphate transporter PHT4;6 causes strong developmental defects, constitutively activated disease resistance mechanisms and altered intracellular phosphate compartmentation in Arabidopsis. Plant J, 72(5): 732-744. |
| [9] | Hassler S, Jung B, Lemke L, Novak O, Strnad M, Martinoia E, Neuhaus H E.2016. Function of the Golgi-located phosphate transporter PHT4;6 is critical for senescence-associated processes in Arabidopsis. J Exp Bot, 67(15): 4671-4684. |
| [10] | Irigoyen S, Karlsson P M, Kuruvilla J, Spetea C, Versaw W K.2011. The sink-specific plastidic phosphate transporter PHT4;2 influences starch accumulation and leaf size in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol, 157(4): 1765-1777. |
| [11] | Jia H F, Ren H Y, Gu M, Zhao J N, Sun S B, Zhang X, Chen J Y, Wu P, Xu G.2011. The phosphate transporter gene OsPht1;8 is involved in phosphate homeostasis in rice. Plant Physiol, 156(3): 1164-1175. |
| [12] | Jia H F, Zhang S T, Wang L Z, Yang Y X, Zhang H Y, Cui H, Shao H F, Xu G H.2017. OsPht1;8, a phosphate transporter, is involved in auxin and phosphate starvation response in rice. J Exp Bot, 68(18): 5057-5068. |
| [13] | Karlsson P M, Herdean A, Adolfsson L, Beebo A, Nziengui H, Irigoyen S, Unnep R, Zsiros O, Nagy G, Garab G, Aronsson H, Versaw W K, Spetea C.2015. The Arabidopsis thylakoid transporter PHT4;1 influences phosphate availability for ATP synthesis and plant growth. Plant J, 84(1): 99-110. |
| [14] | Lapis-Gaza H R, Jost R, Finnegan P M.2014. Arabidopsis PHOSPHATE TRANSPORTER1 genes PHT1;8 and PHT1;9 are involved in root-to-shoot translocation of orthophosphate. BMC Plant Biol, 14: 334. |
| [15] | Li Y T, Zhang J, Zhang X, Fan H M, Gu M, Qu H Y, Xu G H.2015. Phosphate transporter OsPht1;8 in rice plays an important role in phosphorus redistribution from source to sink organs and allocation between embryo and endosperm of seeds. Plant Sci, 230: 23-32. |
| [16] | Lin W Y, Lin S I, Chiou T J.2009. Molecular regulators of phosphate homeostasis in plants. J Exp Bot, 60(5): 1427-1438. |
| [17] | Liu F, Chang X J, Ye Y, Xie W B, Wu P, Lian X M.2011. Comprehensive sequence and whole-life-cycle expression profile analysis of the phosphate transporter gene family in rice. Mol Plant, 4(6): 1105-1122. |
| [18] | Minura T.1999. Regulation of phosphate transport and homeostasis in plant cells. Int Rev Cytol, 191: 149-200. |
| [19] | Miyaji T, Kuromori T, Kakeuchi Y, Yamaji N, Yokosho K, Shimazawa A, Sugimoto E, Omote H, Ma J F, Shinozaki K, Moriyama Y.2015. AtPHT4;4 is a chloroplast-localized ascorbate transporter in Arabidopsis. Nat Commun, 6: 5928. |
| [20] | Mudge S R, Rae A L, Diatloff E, Smith F W.2002. Expression analysis suggests novel roles for members of the Pht1 family of phosphate transporters in Arabidopsis. Plant J, 31(3): 341-353. |
| [21] | Mukherjee P, Banerjee S, Wheeler A, Ratliff L A, Irigoyen S, Garcia L R, Lockless S W, Versaw W K.2015. Live imaging of inorganic phosphate in plants with cellular and subcellular resolution. Plant Physiol, 167(3): 628-638. |
| [22] | Nagarajan V K, Jain A, Poling M D, Lewis A J, Raghothama K G, Smith A P.2011. Arabidopsis Pht1;5 mobilizes phosphate between source and sink organs and influences the interaction between phosphate homeostasis and ethylene signaling. Plant Physiol, 156(3): 1149-1163. |
| [23] | Nelson B K, Cai X, Nebenfuhr A.2007. A multicolored set of in vivo organelle markers for co-localization studies in Arabidopsis and other plants. Plant J, 51(6): 1126-1136. |
| [24] | Pavon L R, Lundh F, Lundin B, Mishra A, Persson B L, Spetea C.2008. Arabidopsis ANTR1 is a thylakoid Na+-dependent phosphate transporter: Functional characterization in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem, 283: 13520-13527. |
| [25] | Pfaffl M W.2001. A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucl Acids Res, 29(9): e45. |
| [26] | Raghothama K G.1999. Phosphate acquisition. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol, 50: 665-693. |
| [27] | Remy E, Cabrito T R, Batista R A, Teixeira M C, Sa-Correia I, Duque P.2012. The Pht1;9 and Pht1;8 transporters mediate inorganic phosphate acquisition by the Arabidopsis thaliana root during phosphorus starvation. New Phytol, 195(2): 356-371. |
| [28] | Rubio V, Linhares F, Solano R, Martín A C, Iglesias J, Leyva A, Paz-Ares J.2001. A conserved MYB transcription factor involved in phosphate starvation signaling both in vascular plants and in unicellular algae. Genes Dev, 15(16): 2122-2133. |
| [29] | Ryu H S, Han M, Lee S K, Cho J I, Ryoo N, Heu S, Lee Y H, Bhoo S H, Wang G L, Hahn T R, Jeon J S.2006. A comprehensive expression analysis of the WRKY gene superfamily in rice plants during defense response. Plant Cell Rep, 25: 836-847. |
| [30] | Secco D, Jabnoune M, Walker H, Shou H X, Wu P, Poirier Y, Whelan J.2013. Spatio-temporal transcript profiling of rice roots and shoots in response to phosphate starvation and recovery. Plant Cell, 25(11): 4285-4304. |
| [31] | Shi S L, Wang D F, Yan Y, Zhang F, Wang H D, Gu M, Sun S B, Xu G H.2013. Function of phosphate transporter OsPHT2;1 in improving phosphate utilization in rice. Chin J Rice Sci, 27(5): 457-465. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [32] | Srivastava S, Upadhyay M K, Srivastava A K, Abdelrahman M, Suprasanna P, Tran L P.2018. Cellular and subcellular phosphate transport machinery in plants. Int J Mol Sci, 19(7): E1914. |
| [33] | Sun S B, Gu M, Cao Y, Huang X P, Zhang X, Ai P H, Zhao J N, Fan X R, Xu G H.2012. A constitutive expressed phosphate transporter, OsPht1;1, modulates phosphate uptake and translocation in phosphate-replete rice. Plant Physiol, 159(4): 1571-1581. |
| [34] | Versaw W K, Harrison M J.2002. A chloroplast phosphate transporter, PHT2;1, influences allocation of phosphate within the plant and phosphate-starvation responses. Plant Cell, 14(8): 1751-1766. |
| [35] | Wang G Y, Shi J L, Ng G, Battle S L, Zhang C, Lu H.2011. Circadian clock-regulated phosphate transporter PHT4;1 plays an important role in Arabidopsis defense. Mol Plant, 4(3): 516-526. |
| [36] | Wang X F, Wang Y F, Pineros M A, Wang Z Y, Wang W X, Li C Y, Wu Z C, Kochian L V, Wu P.2014. Phosphate transporters OsPHT1;9 and OsPHT1;10 are involved in phosphate uptake in rice. Plant Cell Environ, 37(5): 1159-1170. |
| [37] | Wu F H, Shen S C, Lee L Y, Lee S H, Chan M T, Lin C S.2009. Tape-Arabidopsis Sandwich: A simpler Arabidopsis protoplast isolation method. Plant Methods, 5: 16. |
| [38] | Xiang Y, Tang N, Du H, Ye H Y, Xiong L Z.2008. Characterization of OsbZIP23 as a key player of the basic leucine zipper transcription factor family for conferring abscisic acid sensitivity and salinity and drought tolerance in rice. Plant Physiol, 148(4): 1938-1952. |
| [39] | Xu L, Zhao H Y, Wan R J, Liu Y, Xu Z, Tian W, Ruan W Y, Wang F, Deng M J, Wang J M, Dolan L, Luan S, Xue S W, Yi K K.2019. Identification of vacuolar phosphate efflux transporters in land plants. Nat Plants, 5: 84-94. |
| [40] | Yang S Y, Gronlund M, Jakobsen I, Grotemeyer M S, Rentsch D, Miyao A, Hirochika H, Kumar C S, Sundaresan V, Salamin N, Catausan S, Mattes N, Heuer S, Paszkowski U.2012. Nonredundant regulation of rice arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis by two members of the PHOSPHATE TRANSPORTER1 gene family. Plant Cell, 24(10): 4236-4251. |
| [41] | Ye Y, Yuan J, Chang X J, Yang M, Zhang L J, Lu K, Lian X M.2015. The phosphate transporter gene OsPht1;4 is involved in phosphate homeostasis in rice. PLoS One, 10(5): e0126186. |
| [42] | Zhang F, Wu X N, Zhou H M, Wang D F, Jiang T T, Sun Y F, Cao Y, Pei W X, Sun S B, Xu G H.2014. Overexpression of rice phosphate transporter gene OsPT6 enhances phosphate uptake and accumulation in transgenic rice plants. Plant Soil, 384: 259-270. |
| [43] | Zhang F, Sun Y F, Pei W X, Jain A, Sun R, Cao Y, Wu X N, Jiang T T, Zhang L, Fan X R, Chen A Q, Shen Q R, Xu G H, Sun S B.2015. Involvement of OsPht1;4 in phosphate acquisition and mobilization facilitates embryo development in rice. Plant J, 82(4): 556-569. |
| [44] | Zhang Y, Su J B, Duan S, Ao Y, Dai J R, Liu J, Wang P, Li Y G, Liu B, Feng D R, Wang J F, Wang H B.2011. A highly efficient rice green tissue protoplast system for transient gene expression and studying light/chloroplast-related processes. Plant Methods, 7: 30. |
| [45] | Zhang Z L, Liao H, Lucas W J.2014. Molecular mechanisms underlying phosphate sensing, signaling, and adaptation in plants. J Integr Plant Biol, 56(3): 192-220. |
| [46] | Zhu W, Miao Q, Sun D, Yang G D, Wu C G, Huang J G, Zheng C C.2012. The mitochondrial phosphate transporters modulate plant responses to salt stress via affecting ATP and gibberellin metabolism in Arabidopsis thaliana. PLoS One, 7(8): e43530. |
| [1] | Prathap V, Suresh KUMAR, Nand Lal MEENA, Chirag MAHESHWARI, Monika DALAL, Aruna TYAGI. Phosphorus Starvation Tolerance in Rice Through a Combined Physiological, Biochemical and Proteome Analysis [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 8-. |
| [2] | Serena REGGI, Elisabetta ONELLI, Alessandra MOSCATELLI, Nadia STROPPA, Matteo Dell’ANNO, Kiril PERFANOV, Luciana ROSSI. Seed-Specific Expression of Apolipoprotein A-IMilano Dimer in Rice Engineered Lines [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 6-. |
| [3] | Sundus ZAFAR, XU Jianlong. Recent Advances to Enhance Nutritional Quality of Rice [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 4-. |
| [4] | Kankunlanach KHAMPUANG, Nanthana CHAIWONG, Atilla YAZICI, Baris DEMIRER, Ismail CAKMAK, Chanakan PROM-U-THAI. Effect of Sulfur Fertilization on Productivity and Grain Zinc Yield of Rice Grown under Low and Adequate Soil Zinc Applications [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 9-. |
| [5] | FAN Fengfeng, CAI Meng, LUO Xiong, LIU Manman, YUAN Huanran, CHENG Mingxing, Ayaz AHMAD, LI Nengwu, LI Shaoqing. Novel QTLs from Wild Rice Oryza longistaminata Confer Rice Strong Tolerance to High Temperature at Seedling Stage [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 14-. |
| [6] | LIN Shaodan, YAO Yue, LI Jiayi, LI Xiaobin, MA Jie, WENG Haiyong, CHENG Zuxin, YE Dapeng. Application of UAV-Based Imaging and Deep Learning in Assessment of Rice Blast Resistance [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 10-. |
| [7] | Md. Forshed DEWAN, Md. AHIDUZZAMAN, Md. Nahidul ISLAM, Habibul Bari SHOZIB. Potential Benefits of Bioactive Compounds of Traditional Rice Grown in South and South-East Asia: A Review [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 5-. |
| [8] | Raja CHAKRABORTY, Pratap KALITA, Saikat SEN. Phenolic Profile, Antioxidant, Antihyperlipidemic and Cardiac Risk Preventive Effect of Chakhao Poireiton (A Pigmented Black Rice) in High-Fat High-Sugar induced Rats [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 11-. |
| [9] | LI Qianlong, FENG Qi, WANG Heqin, KANG Yunhai, ZHANG Conghe, DU Ming, ZHANG Yunhu, WANG Hui, CHEN Jinjie, HAN Bin, FANG Yu, WANG Ahong. Genome-Wide Dissection of Quan 9311A Breeding Process and Application Advantages [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 7-. |
| [10] | JI Dongling, XIAO Wenhui, SUN Zhiwei, LIU Lijun, GU Junfei, ZHANG Hao, Tom Matthew HARRISON, LIU Ke, WANG Zhiqin, WANG Weilu, YANG Jianchang. Translocation and Distribution of Carbon-Nitrogen in Relation to Rice Yield and Grain Quality as Affected by High Temperature at Early Panicle Initiation Stage [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 12-. |
| [11] | Nazaratul Ashifa Abdullah Salim, Norlida Mat Daud, Julieta Griboff, Abdul Rahim Harun. Elemental Assessments in Paddy Soil for Geographical Traceability of Rice from Peninsular Malaysia [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(5): 486-498. |
| [12] | Monica Ruffini Castiglione, Stefania Bottega, Carlo Sorce, Carmelina SpanÒ. Effects of Zinc Oxide Particles with Different Sizes on Root Development in Oryza sativa [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(5): 449-458. |
| [13] | Tan Jingyi, Zhang Xiaobo, Shang Huihui, Li Panpan, Wang Zhonghao, Liao Xinwei, Xu Xia, Yang Shihua, Gong Junyi, Wu Jianli. ORYZA SATIVA SPOTTED-LEAF 41 (OsSPL41) Negatively Regulates Plant Immunity in Rice [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(5): 426-436. |
| [14] | Ammara Latif, Sun Ying, Pu Cuixia, Noman Ali. Rice Curled Its Leaves Either Adaxially or Abaxially to Combat Drought Stress [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(5): 405-416. |
| [15] | Liu Qiao, Qiu Linlin, Hua Yangguang, Li Jing, Pang Bo, Zhai Yufeng, Wang Dekai. LHD3 Encoding a J-Domain Protein Controls Heading Date in Rice [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(5): 437-448. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||