
Rice Science ›› 2020, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (6): 468-479.DOI: 10.1016/j.rsci.2020.09.004
• Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
Jiajia Wang, Jing Xu, Qian Qian( ), Guangheng Zhang(
), Guangheng Zhang( )
)
Received:2019-12-25
Accepted:2020-05-09
Online:2020-11-28
Published:2020-11-28
About author:#These authors contributed equally to this work
Jiajia Wang, Jing Xu, Qian Qian, Guangheng Zhang. Development of Rice Leaves: How Histocytes Modulate Leaf Polarity Establishment[J]. Rice Science, 2020, 27(6): 468-479.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
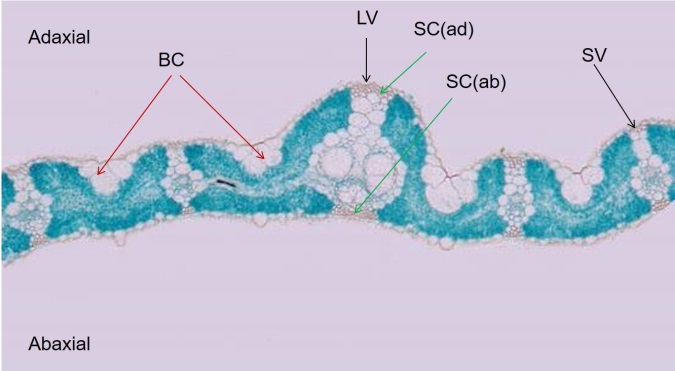
Fig. 1. Overview of tranverse section of rice leaf. BC, Bulliform cell; LV, Large vascular bundle; SV, Small vascular bundle; SC(ad), Sclerenchyma cell (adaxial); SC(ab), Sclerenchyma cell (abaxial).
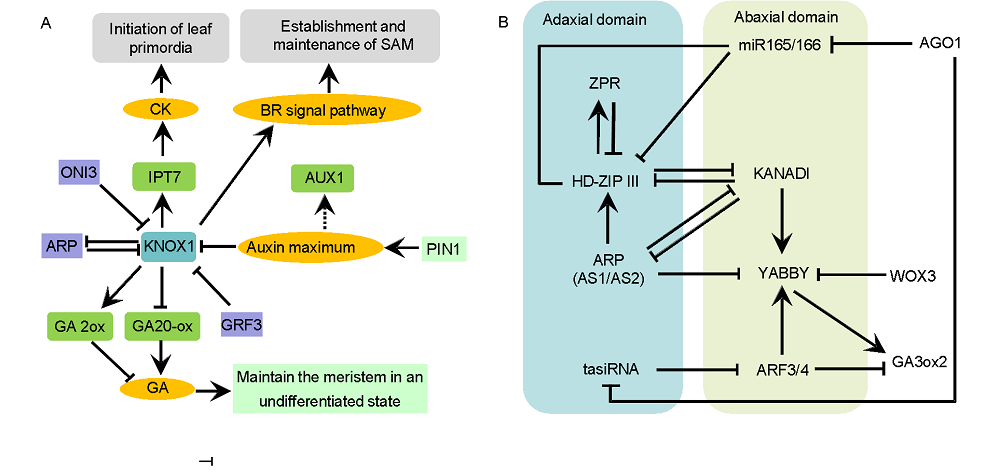
Fig. 2. Genetic and molecular network controlling initiation of leaf primordia (A) and adaxial-abaxial leaf polarity (B).↑ indicates acceleration; indicates inhibition.
| Gene symbol | Gene function | Effect on leaf tissue | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| NAL1/LSCHL4 | Trypsin-like serine/cysteine protease | Cell division, cell expansion and vascular development | |
| OsWOX4 | WUSCHEL-RELATED HOMEOBOX gene family | Cell division and vascular differentiation | |
| SNFL1/NL1 | GATA family | Cell expansion and vascular development | |
| TDD1/OASB1 | Rice anthranilate synthase β-subunit | Cell expansion and vascular development | |
| NRL1/OsCSLD4 | Cellulose synthase-like d4 | Cell expansion and vascular development | |
| LPA1/OsIDD14 | INDETERMINATE DOMAIN protein | Cell division and cell expansion | |
| OsJar1/OsGH3-5 | Jasmonic acid-amino acid synthetase | Cell division | |
| SG1 | Unknown | Cell division | |
| OsARF18/OsARF10 | Auxin response factor | Cell division | |
| SGL1 | SG1-like protein 1 | Cell division | |
| D1/RGA1 | GTP-binding α-subunit of heterotrimeric G protein | Cell division | |
| STD1 | A phragmoplast-associated kinesin-related protein | Cell division | |
| OsSAUR45 | Small auxin-up RNA | Cell expansion | |
| OsVPE3 | Vacuolar processing enzyme/cysteine proteinases | Cell expansion | |
| RPL3B/RML1 | Ribosome large subunit protein 3b | Cell expansion | |
| OsCCC1 | Cation-chloride cotransporter | Cell expansion | |
| GL7/GW7/OsFLW7 | LONGIFOLIA protein | Cell expansion | |
| GL7NR | Negative regulator of GL7 | Cell expansion | |
| DGL1 | Microtubule-severing katanin-like protein | Cell expansion | |
| OsARF19/OsARF7a | Auxin response factor | Cell expansion | |
| OsOFP2 | Ovate family protein 2 | Cell expansion | |
| OsGIF1 | GRF-interacting factor 1, putative, expressed | Cell expansion | |
| OsNAAL1/CHR729 | Chromodomain helicase/ATPase DNA-binding protein | Vascular development | |
| Osa-miR319a | MicroRNA319 | Vascular development | |
| Osa-miR319b | MicroRNA319 | Vascular development | |
| NAL9/VYL/ClpP | Plastidic caseinolytic protease | Vascular development | |
| OsIAA3 | Rice auxin/indole acetic acid gene | Vascular development | |
| OsWOX3A | WUSCHEL-related homeobox 3A | Vascular development | |
| OsARVL4 | Insoluble protein, putative, expressed | Vascular development | |
| REL2 | Unknown function protein containing DUF630 and DUF632 domains | Bulliform cell development | |
| REL1 | Unknown | Bulliform cell development | |
| ACL1 | With unknown conserved functional domains | Bulliform cell development | |
| OsZHD1/ACL-D | Zn-finger transcription factor | Bulliform cell development | |
| Roc5/oul1 | Homeodomain leucine zipper class IV gene | Bulliform cell development | |
| LRRK1 | Receptor like cytoplasmic kinases (RLCKs) | Bulliform cell development | |
| OsLBD3-7 | Lateral organ boundaries domain gene | Bulliform cell development | |
| OSHB4/OsHox32 | Class III homeodomain Leu zipper (HD-ZIP class III) | Bulliform cell development | |
| OsYABBY6 | YABBY gene | Bulliform cell development | |
| OsCOW1/NAL7 | Flavin-containing monooxygenase | Bulliform cell and vascular development | |
| ADL1/OsDEK1 | Plant-specific calpain-like cysteine proteinase | Sclerenchyma cell development | |
| OsAGO1b | AGO gene | Sclerenchyma cell development | |
| SLL1 | SHAQKYF class MYB family transcription factor | Sclerenchyma cell development | |
| OsYAB1/OsYABBY1 | YABBY gene | Sclerenchyma cell development | |
| SRL2/AVB/NRL2 | A protein with unknown function | Sclerenchyma cell development | |
| OsMYB103L/CEF1 | R2R3-MYB transcription factor | Cell wall development | |
| SRS3/OsKinesin-13A | Microtubule depolymerase | Cell wall development | |
| OsEXPB2 | β-expansin gene | Cell wall relaxation | |
| OsSND2 | No apical meristem protein, putative, expressed | Thickness of sclerenchyma cell wall | |
| RL14 | 2OG-Fe (II) oxygenase family protein | Secondary cell wall formation | |
| CLD1/SRL1 | Glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored protein | Epidermal cell development | |
| OsKS2/OsKSL2 | Ent-beyerene synthase | Mesophyll cell development | |
| ONI3/Mini1 | Long-chain fatty acid ω-alcohol dehydrogenase | Leaf primordium development | |
| WSL1 | β-ketoacyl CoA synthase | Leaf wax biosynthesis | |
| CFL1 | WW domain protein | Cuticle development | |
| OsCHR4 | CHD3 family chromatin remodeler | Cuticular wax biosynthesis |
Table 1 Lists of genes controlling rice leaf morphology.
| Gene symbol | Gene function | Effect on leaf tissue | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| NAL1/LSCHL4 | Trypsin-like serine/cysteine protease | Cell division, cell expansion and vascular development | |
| OsWOX4 | WUSCHEL-RELATED HOMEOBOX gene family | Cell division and vascular differentiation | |
| SNFL1/NL1 | GATA family | Cell expansion and vascular development | |
| TDD1/OASB1 | Rice anthranilate synthase β-subunit | Cell expansion and vascular development | |
| NRL1/OsCSLD4 | Cellulose synthase-like d4 | Cell expansion and vascular development | |
| LPA1/OsIDD14 | INDETERMINATE DOMAIN protein | Cell division and cell expansion | |
| OsJar1/OsGH3-5 | Jasmonic acid-amino acid synthetase | Cell division | |
| SG1 | Unknown | Cell division | |
| OsARF18/OsARF10 | Auxin response factor | Cell division | |
| SGL1 | SG1-like protein 1 | Cell division | |
| D1/RGA1 | GTP-binding α-subunit of heterotrimeric G protein | Cell division | |
| STD1 | A phragmoplast-associated kinesin-related protein | Cell division | |
| OsSAUR45 | Small auxin-up RNA | Cell expansion | |
| OsVPE3 | Vacuolar processing enzyme/cysteine proteinases | Cell expansion | |
| RPL3B/RML1 | Ribosome large subunit protein 3b | Cell expansion | |
| OsCCC1 | Cation-chloride cotransporter | Cell expansion | |
| GL7/GW7/OsFLW7 | LONGIFOLIA protein | Cell expansion | |
| GL7NR | Negative regulator of GL7 | Cell expansion | |
| DGL1 | Microtubule-severing katanin-like protein | Cell expansion | |
| OsARF19/OsARF7a | Auxin response factor | Cell expansion | |
| OsOFP2 | Ovate family protein 2 | Cell expansion | |
| OsGIF1 | GRF-interacting factor 1, putative, expressed | Cell expansion | |
| OsNAAL1/CHR729 | Chromodomain helicase/ATPase DNA-binding protein | Vascular development | |
| Osa-miR319a | MicroRNA319 | Vascular development | |
| Osa-miR319b | MicroRNA319 | Vascular development | |
| NAL9/VYL/ClpP | Plastidic caseinolytic protease | Vascular development | |
| OsIAA3 | Rice auxin/indole acetic acid gene | Vascular development | |
| OsWOX3A | WUSCHEL-related homeobox 3A | Vascular development | |
| OsARVL4 | Insoluble protein, putative, expressed | Vascular development | |
| REL2 | Unknown function protein containing DUF630 and DUF632 domains | Bulliform cell development | |
| REL1 | Unknown | Bulliform cell development | |
| ACL1 | With unknown conserved functional domains | Bulliform cell development | |
| OsZHD1/ACL-D | Zn-finger transcription factor | Bulliform cell development | |
| Roc5/oul1 | Homeodomain leucine zipper class IV gene | Bulliform cell development | |
| LRRK1 | Receptor like cytoplasmic kinases (RLCKs) | Bulliform cell development | |
| OsLBD3-7 | Lateral organ boundaries domain gene | Bulliform cell development | |
| OSHB4/OsHox32 | Class III homeodomain Leu zipper (HD-ZIP class III) | Bulliform cell development | |
| OsYABBY6 | YABBY gene | Bulliform cell development | |
| OsCOW1/NAL7 | Flavin-containing monooxygenase | Bulliform cell and vascular development | |
| ADL1/OsDEK1 | Plant-specific calpain-like cysteine proteinase | Sclerenchyma cell development | |
| OsAGO1b | AGO gene | Sclerenchyma cell development | |
| SLL1 | SHAQKYF class MYB family transcription factor | Sclerenchyma cell development | |
| OsYAB1/OsYABBY1 | YABBY gene | Sclerenchyma cell development | |
| SRL2/AVB/NRL2 | A protein with unknown function | Sclerenchyma cell development | |
| OsMYB103L/CEF1 | R2R3-MYB transcription factor | Cell wall development | |
| SRS3/OsKinesin-13A | Microtubule depolymerase | Cell wall development | |
| OsEXPB2 | β-expansin gene | Cell wall relaxation | |
| OsSND2 | No apical meristem protein, putative, expressed | Thickness of sclerenchyma cell wall | |
| RL14 | 2OG-Fe (II) oxygenase family protein | Secondary cell wall formation | |
| CLD1/SRL1 | Glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored protein | Epidermal cell development | |
| OsKS2/OsKSL2 | Ent-beyerene synthase | Mesophyll cell development | |
| ONI3/Mini1 | Long-chain fatty acid ω-alcohol dehydrogenase | Leaf primordium development | |
| WSL1 | β-ketoacyl CoA synthase | Leaf wax biosynthesis | |
| CFL1 | WW domain protein | Cuticle development | |
| OsCHR4 | CHD3 family chromatin remodeler | Cuticular wax biosynthesis |
| [1] | Akiba T, Hibara K I, Kimura F, Tsuda K, Shibata K, Ishibashi M, Moriya C, Nakagawa K, Kurata N, Itoh J, Ito Y.2014. Organ fusion and defective shoot development in oni3 mutants of rice. Plant Cell Physiol, 55(1): 42-51. |
| [2] | Byrne M E, Barley R, Curtis M, Arroyo J M, Dunham M, Hudson A, Martienssen R A.2000. Asymmetric leaves1 mediates leaf patterning and stem cell function in Arabidopsis. Nature, 408: 967-971. |
| [3] | Byrne M E, Simorowski J, Martienssen R A.2002. ASYMMETRIC LEAVES1 reveals knox gene redundancy in Arabidopsis. Development, 129(8): 1957-1965. |
| [4] | Chen K, Guo T, Li X M, Yang Y B, Dong N Q, Shi C L, Ye W W, Shan J X, Lin H X.2019. NAL8 encodes a prohibitin that contributes to leaf and spikelet development by regulating mitochondria and chloroplasts stability in rice. BMC Plant Biol, 19(1): 395. |
| [5] | Chen Q L, Xie Q J, Gao J, Wang W Y, Sun B, Liu B H, Zhu H T, Peng H F, Zhao H B, Liu C H, Wang J, Zhang J L, Zhang G Q, Zhang Z M.2015. Characterization of Rolled and Erect Leaf 1 in regulating leave morphology in rice. J Exp Bot, 66(19): 6047-6058. |
| [6] | Chen T, Chen Z, Sathe A P, Zhang Z H, Li L J, Shang H H, Tang S Q, Zhang X B, Wu J L.2019. Characterization of a novel gain- of-function spotted-leaf mutant with enhanced disease resistance in rice. Rice Sci, 26(6): 372-383. |
| [7] | Chen Z C, Yamaji N, Fujii-Kashino M, Ma J F.2016. A cation- chloride cotransporter gene is required for cell elongation and osmoregulation in rice. Plant Physiol, 171(1): 494-507. |
| [8] | Cho S H, Kang K, Lee S H, Lee I J, Paek N C.2016. OsWOX3A is involved in negative feedback regulation of the gibberellic acid biosynthetic pathway in rice (Oryza sativa). J Exp Bot, 67(6): 1677-1687. |
| [9] | Dai M Q, Hu Y F, Zhao Y, Liu H F, Zhou D X.2007a. A WUSCHEL- LIKE HOMEOBOX gene represses a YABBY gene expression required for rice leaf development. Plant Physiol, 144(1): 380-390. |
| [10] | Dai M Q, Zhao Y, Ma Q, Hu Y F, Hedden P, Zhang Q F, Zhou D X.2007b. The rice YABBY1 gene is involved in the feedback regulation of gibberellin metabolism. Plant Physiol, 144(1): 121-133. |
| [11] | Deng Z Y, Liu L T, Li T, Yan S, Kuang B J, Huang S J, Yan C J, Wang T.2015. OsKinesin-13A is an active microtubule depolymerase involved in glume length regulation via affecting cell elongation. Sci Rep, 5: 9457. |
| [12] | Ding Z Q, Lin Z F, Li Q, Wu H, Xiang C Y, Wang J F.2015. DNL1, encodes cellulose synthase-like D4, is a major QTL for plant height and leaf width in rice(Oryza sativa L.). Biochem Biophy Res Commun, 457(2): 133-140. |
| [13] | Fang J J, Yuan S J, Li C C, Jiang D, Zhao L L, Peng L X, Zhao J F, Zhang W H, Li X Y.2018. Reduction of ATPase activity in the rice kinesin protein Stemless Dwarf1 inhibits cell division and organ development. Plant J, 96(3): 620-634. |
| [14] | Fang L K, Zhao F M, Cong Y F, Sang X C, Du Q, Wang D Z, Li Y F, Ling Y H, Yang Z L, He G H.2012. Rolling-leaf 14 is a 2OG-Fe (II) oxygenase family protein that modulates rice leaf rolling by affecting secondary cell wall formation in leaves. Plant Biotechnol J, 10(5): 524-532. |
| [15] | Fang Y X, Hu J, Xu J, Yu H P, Shi Z Y, Xiong G S, Zhu L, Zeng D L, Zhang G H, Gao Z Y, Dong G J, Yan M X, Guo L B, Wang Y H, Qian Q.2015. Identification and characterization of Mini1, a gene regulating rice shoot development. J Integr Plant Biol, 57(2): 151-161. |
| [16] | Fujino K, Matsuda Y, Ozawa K, Nishimura T, Koshiba T, Fraaije M W, Sekiguchi H.2008. NARROW LEAF 7 controls leaf shape mediated by auxin in rice. Mol Genet Genom, 279(5): 499-507. |
| [17] | Fujisawa Y, Kato T, Ohki S, Ishikawa A, Kitano H, Sasaki T, Asahi T, Iwasaki Y.1999. Suppression of the heterotrimeric G protein causes abnormal morphology, including dwarfism, in rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 96(13): 7575-7580. |
| [18] | Guenot B, Bayer E, Kierzkowski D, Smith R S, Mandel T, Zadnikova P, Benkova E, Kuhlemeier C.2012. Pin1-independent leaf initiation in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol, 159(4): 1501-1510. |
| [19] | Guo T T, Wang D F, Fang J J, Zhao J F, Yuan S J, Xiao L T, Li X Y.2019. Mutations in the rice OsCHR4 gene, encoding a CHD3 family chromatin remodeler, induce narrow and rolled leaves with increased cuticular wax. Int J Mol Sci, 20(10): 2567. |
| [20] | Hasson A, Blein T, Laufs P.2010. Leaving the meristem behind: The genetic and molecular control of leaf patterning and morphogenesis. Compt Rendus Biol, 333(4): 350-360. |
| [21] | Hay A, Tsiantis M.2009. A KNOX family TALE. Curr Opin Plant Biol, 12(5): 593-598. |
| [22] | He P L, Wang X W, Zhang X B, Jiang Y D, Tian W J, Zhang X Q, Li Y Y, Sun Y, Xie J, Ni J L, He G H, Sang X C.2018. Short and narrow flag leaf1, a GATA zinc finger domain-containing protein, regulates flag leaf size in rice (Oryza sativa). BMC Plant Biol, 18(1): 273. |
| [23] | He Z S, Zeng J, Ren Y, Chen D, Li W J, Gao F Y, Cao Y, Luo T, Yuan G Q, Wu X H, Liang Y Y, Deng Q M, Wang S Q, Zheng A P, Zhu J, Liu H N, Wang L X, Li P, Li S C.2017. OsGIF1 positively regulates the sizes of stems, leaves, and grains in rice. Front Plant Sci, 8: 1730. |
| [24] | Hibara K I, Obara M, Hayashida E, Abe M, Ishimaru T, Satoh H, Itoh J I, Nagato Y.2009. The ADAXIALIZED LEAF1 gene functions in leaf and embryonic pattern formation in rice. Dev Biol, 334(2): 345-354. |
| [25] | Hu J, Zhu L, Zeng D L, Gao Z Y, Guo L B, Fang Y X, Zhang G H, Dong G J, Yan M X, Liu J, Qian Q.2010. Identification and characterization of NARROW AND ROLLED LEAF 1, a novel gene regulating leaf morphology and plant architecture in rice. Plant Mol Biol, 73(3): 283-292. |
| [26] | Huang J, Li Z Y, Zhao D Z.2016. Deregulation of the osmiR160 target gene OsARF18 causes growth and developmental defects with an alteration of auxin signaling in rice. Sci Rep, 6: 29938. |
| [27] | Ishiwata A, Ozawa M, Nagasaki H, Kato M, Noda Y, Yamaguchi T, Nosaka M, Shimizu-Sato S, Nagasaki A, Maekawa M, Hirano H Y, Sato Y.2013. Two WUSCHEL-related homeobox genes, narrow leaf2 and narrow leaf3, control leaf width in rice. Plant Cell Physiol, 54(5): 779-792. |
| [28] | Ito Y, Eiguchi M, Kurata N.2001. KNOX homeobox genes are sufficient in maintaining cultured cells in an undifferentiated state in rice. Genesis, 30(4): 231-238. |
| [29] | Itoh J I, Sato Y, Nagato Y.2008. The SHOOT ORGANIZATION2 gene coordinates leaf domain development along the central- marginal axis in rice. Plant Cell Physiol, 49(8): 1226-1236. |
| [30] | Izawa Y, Takayanagi Y, Inaba N, Abe Y, Minami M, Fujisawa Y, Kato H, Ohki S, Kitano H, Iwasaki Y.2010. Function and expression pattern of the alpha subunit of the heterotrimeric G protein in rice. Plant Cell Physiol, 51(2): 271-281. |
| [31] | Ji S H, Gururani M A, Lee J W, Ahn B O, Chun S C.2014. Isolation and characterisation of a dwarf rice mutant exhibiting defective gibberellins biosynthesis. Plant Biol, 16(2): 428-439. |
| [32] | Jiang D, Fang J J, Lou L M, Zhao J F, Yuan S J, Yin L, Sun W, Peng L X, Guo B T, Li X Y.2015. Characterization of a null allelic mutant of the rice NAL1 gene reveals its role in regulating cell division. PLoS One, 10(2): e0118169. |
| [33] | Kalve S, de Vos D, Beemster G T.2014. Leaf development: A cellular perspective. Front Plant Sci, 5: 362. |
| [34] | Kawakatsu T, Taramino G, Itoh J, Allen J, Sato Y, Hong S K, Yule R, Nagasawa N, Kojima M, Kusaba M, Sakakibara H, Sakai H, Nagato Y.2009. PLASTOCHRON3/GOLIATH encodes a glutamate carboxypeptidase required for proper development in rice. Plant J, 58(6): 1028-1040. |
| [35] | Komorisono M, Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Aichi I, Hasegawa Y, Ashikari M, Kitano H, Matsuoka M, Sazuka T.2005. Analysis of the rice mutant dwarf and gladius leaf 1: Aberrant katanin-mediated microtubule organization causes up-regulation of gibberellin biosynthetic genes independently of gibberellin signaling. Plant Physiol, 138(4): 1982-1993. |
| [36] | Kuijt S J H, Greco R, Agalou A, Shao J X, Hoen C C J, Övernäs E, Osnato M, Curiale S, Meynard D, van Gulik R, de Faria Maraschin S, Atallah M, de Kam R J, Lamers G E M, Guiderdoni E, Rossini L, Meijer A H, Ouwerkerk P B F.2014. Interaction between the GROWTH-REGULATING FACTOR and KNOTTED1-LIKE HOMEOBOX families of transcription factors. Plant Physiol, 164(4): 1952-1966. |
| [37] | Li C, Zou X H, Zhang C Y, Shao Q H, Liu J, Liu B, Li H Y, Zhao T.2016. OsLBD3-7 overexpression induced adaxially rolled leaves in rice. PLoS One, 11(6): e0156413. |
| [38] | Li L, Shi Z Y, Li L, Shen G Z, Wang X Q, An L S, Zhang J L.2010. Overexpression of ACL1 (abaxially curled leaf 1) increased bulliform cells and induced abaxial curling of leaf blades in rice. Mol Plant, 3(5): 807-817. |
| [39] | Li W, Wu C, Hu G C, Xing L, Qian W J, Si H M, Sun Z X, Wang X C, Fu Y P, Liu W Z.2013. Characterization and fine mapping of a novel rice narrow leaf mutant nal9. J Integr Plant Biol, 55(11): 1016-1025. |
| [40] | Li W Q, Zhang M J, Gan P F, Qiao L, Yang S Q, Miao H, Wang G F, Zhang M M, Liu W T, Li H F, Shi C H, Chen K M.2017. CLD1/SRL1 modulates leaf rolling by affecting cell wall formation, epidermis integrity and water homeostasis in rice. Plant J, 92(5): 904-923. |
| [41] | Li Y H, Yang Y Q, Liu Y, Li D X, Zhao Y H, Li Z J, Liu Y, Jiang D G, Li J, Zhou H, Chen J H, Zhuang C X, Liu Z L.2019. Overexpression of OsAGO1b induces adaxially rolled leaves by affecting leaf abaxial sclerenchymatous cell development in rice. Rice, 12(1): 60. |
| [42] | Li Y Y, Shen A, Xiong W, Sun Q L, Luo Q, Song T, Li Z L, Luan W J.2016. Overexpression of OsHox32 results in pleiotropic effects on plant type architecture and leaf development in rice. Rice, 9(1): 46. |
| [43] | Lin L H, Zhao Y F, Liu F, Chen Q, Qi J C.2019. Narrow leaf 1 (NAL1) regulates leaf shape by affecting cell expansion in rice(Oryza sativa L.). Biochem Biophy Res Commun, 516(3): 957-962. |
| [44] | Liu H Y, Wang W Q, He A B, Nie L X.2018. Correlation of leaf and root senescence during ripening in dry seeded and transplanted rice. Rice Sci, 25(5): 279-285. |
| [45] | Liu X F, Li M, Liu K, Tang D, Sun M F, Li Y F, Shen Y, Du G J, Cheng Z K.2016. Semi-Rolled Leaf2 modulates rice leaf rolling by regulating abaxial side cell differentiation. J Exp Bot, 67(8): 2139-2150. |
| [46] | Lu W Y, Deng M J, Guo F, Wang M Q, Zeng Z H, Han N, Yang Y N, Zhu M Y, Bian H W.2016. Suppression of OsVPE3 enhances salt tolerance by attenuating vacuole rupture during programmed cell death and affects stomata development in rice. Rice, 9(1): 65. |
| [47] | Ma L, Sang X C, Zhang T, Yu Z Y, Li Y F, Zhao F M, Wang Z W, Wang Y T, Yu P, Wang N, Zhang C W, Ling Y H, Yang Z L, He G H.2017. ABNORMAL VASCULAR BUNDLES regulates cell proliferation and procambium cell establishment during aerial organ development in rice. New Phytol, 213(1): 275-286. |
| [48] | Matsumoto H, Yasui Y, Kumamaru T, Hirano H Y.2018. Characterization of a half-pipe-like leaf1 mutant that exhibits a curled leaf phenotype. Genes Genet Syst, 92(6): 287-291. |
| [49] | Mimura M, Nagato Y, Itoh J I.2012. Rice PLASTOCHRON genes regulate leaf maturation downstream of the gibberellin signal transduction pathway. Planta, 235(5): 1081-1089. |
| [50] | Mimura M, Itoh J I.2014. Genetic interaction between rice PLASTOCHRON genes and the gibberellin pathway in leaf development. Rice, 7(1): 25. |
| [51] | Mishra S S, Panda D.2017. Leaf traits and antioxidant defense for drought tolerance during early growth stage in some popular traditional rice landraces from Koraput, India. Rice Sci, 24(4): 207-217. |
| [52] | Miyoshi K, Ahn B O, Kawakatsu T, Ito Y, Itoh J I, Nagato Y, Kurata N.2004. PLASTOCHRON1, a timekeeper of leaf initiation in rice, encodes cytochrome P450. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 101(3): 875-880. |
| [53] | Nakagawa H, Tanaka A, Tanabata T, Ohtake M, Fujioka S, Nakamura H, Ichikawa H, Mori M.2012. Short grain1 decreases organ elongation and brassinosteroid response in rice. Plant Physiol, 158(3): 1208-1219. |
| [54] | Nakamura A, Umemura I, Gomi K, Hasegawa Y, Kitano H, Sazuka T, Matsuoka M.2006. Production and characterization of auxin- insensitive rice by overexpression of a mutagenized rice IAA protein. Plant J, 46(2): 297-306. |
| [55] | Ohmori Y, Tanaka W, Kojima M, Sakakibara H, Hirano H Y.2013. WUSCHEL-RELATED HOMEOBOX4 is involved in meristem maintenance and is negatively regulated by the CLE gene FCP1 in rice. Plant Cell, 25(1): 229-241. |
| [56] | Piazza P, Jasinski S, Tsiantis M.2005. Evolution of leaf developmental mechanisms. New Phytol, 167(3): 693-710. |
| [57] | Postma-Haarsma A D, Verwoert I I, Stronk O P, Koster J, Lamers G E, Hoge J H, Meijer A H.1999. Characterization of the KNOX class homeobox genes Oskn2 and Oskn3 identified in a collection of cDNA libraries covering the early stages of rice embryogenesis. Plant Mol Biol, 39(2): 257-271. |
| [58] | Qiu Z N, Zhu L, He L, Chen D D, Zeng D L, Chen G, Hu J, Zhang G H, Ren D Y, Dong G J, Gao Z Y, Shen L, Zhang Q, Guo L B, Qian Q.2019. DNA damage and reactive oxygen species cause cell death in the rice local lesions 1 mutant under high light and high temperature. New Phytol, 222(1): 349-365. |
| [59] | Sato Y, Hong S K, Tagiri A, Kitano H, Yamamoto N, Nagato Y, Matsuoka M.1996. A rice homeobox gene, OSH1, is expressed before organ differentiation in a specific region during early embryogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 93(15): 8117-8122. |
| [60] | Sazuka T, Kamiya N, Nishimura T, Ohmae K, Sato Y, Imamura K, Nagato Y, Koshiba T, Nagamura Y, Ashikari M, Kitano H, Matsuoka M.2009. A rice tryptophan deficient dwarf mutant, tdd1, contains a reduced level of indole acetic acid and develops abnormal flowers and organless embryos. Plant J, 60(2): 227-241. |
| [61] | Schmitz A J, Begcy K, Sarath G, Walia H.2015. Rice Ovate Family Protein 2 (OFP2) alters hormonal homeostasis and vasculature development. Plant Sci, 241: 177-188. |
| [62] | Su Y H, Liu Y B, Zhang X S.2011. Auxin-cytokinin interaction regulates meristem development. Mol Plant, 4(4): 616-625. |
| [63] | Toriba T, Harada K, Takamura A, Nakamura H, Ichikawa H, Suzaki T, Hirano H Y.2007. Molecular characterization the YABBY gene family in Oryza sativa and expression analysis of OsYABBY1. Mol Genet Genom, 277(5): 457-468. |
| [64] | Tsuda K, Ito Y, Sato Y, Kurata N.2011. Positive autoregulation of a KNOX gene is essential for shoot apical meristem maintenance in rice. Plant Cell, 23(12): 4368-4381. |
| [65] | Tsuda K, Kurata N, Ohyanagi H, Hake S.2014. Genome-wide study of KNOX regulatory network reveals brassinosteroid catabolic genes important for shoot meristem function in rice. Plant Cell, 26(9): 3488-3500. |
| [66] | Wang L, Xu J, Nian J Q, Shen N W, Lai K K, Hu J, Zeng D L, Ge C W, Fang Y X, Zhu L, Qian Q, Zhang G H.2016. Characterization and fine mapping of the rice gene OsARVL4 regulating leaf morphology and leaf vein development. Plant Growth Regul, 78(3): 345-356. |
| [67] | Wang S T, Sun X L, Hoshino Y, Yu Y, Jia B, Sun Z W, Sun M Z, Duan X B, Zhu Y M.2014. MicroRNA319 positively regulates cold tolerance by targeting OsPCF6 and OsTCP21 in rice(Oryza sativa L.). PLoS One, 9(3): e91357. |
| [68] | Wang Y X, Xiong G S, Hu J, Jiang L, Yu H, Xu J, Fang Y X, Zeng L J, Xu E B, Xu J, Ye W J, Meng X B, Liu R F, Chen H Q, Jing Y H, Wang Y H, Zhu X D, Li J Y, Qian Q.2015. Copy number variation at the GL7 locus contributes to grain size diversity in rice. Nat Genet, 47(8): 944-948. |
| [69] | Woo Y M, Park H J, Su’udi M, Yang J I, Park J J, Back K, Park Y M, An G.2007. Constitutively wilted 1, a member of the rice YUCCA gene family, is required for maintaining water homeostasis and an appropriate root to shoot ratio. Plant Mol Biol, 65: 125-136. |
| [70] | Wu R H, Li S B, He S, Wassmann F, Yu C H, Qin G J, Schreiber L, Qu L J, Gu H Y.2011. CFL1, a WW domain protein, regulates cuticle development by modulating the function of HDG1, a class IV homeodomain transcription factor, in rice and Arabidopsis. Plant Cell, 23(9): 3392-3411. |
| [71] | Wu X R, Tang D, Li M, Wang K J, Cheng Z K.2013. Loose Plant Architecture1, an INDETERMINATE DOMAIN protein involved in shoot gravitropism, regulates plant architecture in rice. Plant Physiol, 161(1): 317-329. |
| [72] | Xia M L, Tang D Y, Yang Y Z, Li Y X, Wang W W, Lü H, Liu X M, Lin J Z.2017. Preliminary study on the rice OsYABBY6 gene involving in the regulation of leaf development. Life Sci Res, 21(1): 23-30. |
| [73] | Xiang J J, Zhang G H, Qian Q, Xue H W.2012. Semi-rolled leaf1 encodes a putative glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored protein and modulates rice leaf rolling by regulating the formation of bulliform cells. Plant Physiol, 159(4): 1488-1500. |
| [74] | Xiong G S, Hu X M, Jiao Y Q, Yu Y C, Chu C C, Li J Y, Qian Q, Wang Y H.2006. Leafy head2, which encodes a putative RNA- binding protein, regulates shoot development of rice. Cell Res, 16(3): 267-276. |
| [75] | Xu J, Wang L, Zhou M Y, Zeng D L, Hu J, Zhu L, Ren D Y, Dong G J, Gao Z Y, Guo L B, Qian Q, Zhang W Z, Zhang G H.2017. Narrow albino leaf 1 is allelic to CHR729, regulates leaf morphogenesis and development by affecting auxin metabolism in rice. Plant Growth Regul, 82(1): 175-186. |
| [76] | Xu Y, Wang Y H, Long Q Z, Huang J X, Wang Y L, Zhou K N, Zheng M, Sun J, Chen H, Chen S C, Jiang L, Wang C M, Wan J M.2014. Overexpression of OsZHD1, a zinc finger homeodomain class homeobox transcription factor, induces abaxially curled and drooping leaf in rice. Planta, 239(4): 803-816. |
| [77] | Xu Y X, Xiao M Z, Liu Y, Fu J L, He Y, Jiang D A.2017. The small auxin-up RNA OsSAUR45 affects auxin synthesis and transport in rice. Plant Mol Biol, 94: 97-107. |
| [78] | Yang C H, Li D Y, Mao D H, Liu X, Ji C J, Li X B, Zhao X F, Cheng Z K, Chen C Y, Zhu L H.2013. Overexpression of microRNA319 impacts leaf morphogenesis and leads to enhanced cold tolerance in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Cell Environ, 36(12): 2207-2218. |
| [79] | Yang C H, Li D Y, Liu X, Ji C J, Hao L L, Zhao X F, Li X B, Chen C Y, Cheng Z K, Zhu L H.2014. OsMYB103L, an R2R3-MYB transcription factor, influences leaf rolling and mechanical strength in rice (Oryza sativa L.). BMC Plant Biol, 14: 158. |
| [80] | Yang S Q, Li W Q, Miao H, Gan P F, Qiao L, Chang Y L, Shi C H, Chen K M.2016. REL2, a gene encoding an unknown function protein which contains DUF630 and DUF632 domains controls leaf rolling in rice. Rice, 9(1): 37. |
| [81] | Yasui Y, Ohmori Y, Takebayashi Y, Sakakibara H, Hirano H Y.2018. WUSCHEL-RELATED HOMEOBOX4 acts as a key regulator in early leaf development in rice. PLoS Genet, 14(4): e1007365. |
| [82] | Ye Y F, Liu B M, Zhao M, Wu K, Cheng W M, Chen X B, Liu Q, Liu Z, Fu X D, Wu Y J.2015. CEF1/OsMYB103L is involved in GA-mediated regulation of secondary wall biosynthesis in rice. Plant Mol Biol, 89: 385-401. |
| [83] | Ye Y F, Wu K, Chen J F, Liu Q, Wu Y J, Liu B M, Fu X D.2018. OsSND2, a NAC family transcription factor, is involved in secondary cell wall biosynthesis through regulating MYBs expression in rice. Rice, 11(1): 36. |
| [84] | Yu D M, Ranathunge K, Huang H S, Pei Z Y, Franke R, Schreiber L, He C Z.2008. Wax Crystal-Sparse Leaf1 encodes a beta- ketoacyl CoA synthase involved in biosynthesis of cuticular waxes on rice leaf. Planta, 228(4): 675-685. |
| [85] | Zhang G H, Xu Q, Zhu X D, Qian Q, Xue H W.2009. SHALLOT-LIKE1 is a KANADI transcription factor that modulates rice leaf rolling by regulating leaf abaxial cell development. Plant Cell, 21(3): 719-735. |
| [86] | Zhang G H, Li S Y, Wang L, Ye W J, Zeng D L, Rao Y C, Peng Y L, Hu J, Yang Y L, Xu J, Ren D Y, Gao Z Y, Zhu L, Dong G J, Hu X M, Yan M X, Guo L B, Li C Y, Qian Q.2014. LSCHL4 from japonica cultivar, which is allelic to NAL1, increases yield of indica super rice 93-11. Mol Plant, 7(8): 1350-1364. |
| [87] | Zhang J J, Wu S Y, Jiang L, Wang J L, Zhang X, Guo X P, Wu C Y, Wan J M.2015. A detailed analysis of the leaf rolling mutant sll2 reveals complex nature in regulation of bulliform cell development in rice(Oryza sativa L.). Plant Biol, 17(2): 437-448. |
| [88] | Zhang J S, Zhang H, Srivastava A K, Pan Y J, Bai J J, Fang J J, Shi H Z, Zhu J K.2018. Knockdown of rice microRNA166 confers drought resistance by causing leaf rolling and altering stem xylem development. Plant Physiol, 176(3): 2082-2094. |
| [89] | Zhang S N, Wang S K, Xu Y X, Yu C L, Shen C J, Qian Q, Geisler M, Jiang D A, Qi Y H.2015. The auxin response factor, OsARF19, controls rice leaf angles through positively regulating OsGH3-5 and OsBRI1. Plant Cell Environ, 38(4): 638-654. |
| [90] | Zhao S S, Zhao L, Liu F X, Wu Y Z, Zhu Z F, Sun C Q, Tan L B.2016. NARROW AND ROLLED LEAF 2 regulates leaf shape, male fertility, and seed size in rice. J Integr Plant Biol, 58(12): 983-996. |
| [91] | Zheng M, Wang Y H, Liu X, Sun J, Wang Y L, Xu Y, Lv J, Long W H, Zhu X P, Guo X P, Jiang L, Wang C M, Wan J M.2016. The RICE MINUTE-LIKE1 (RML1) gene, encoding a ribosomal large subunit protein L3B, regulates leaf morphology and plant architecture in rice. J Exp Bot, 67(11): 3457-3469. |
| [92] | Zhou Y B, Wang D, Wu T, Yang Y Z, Liu C, Yan L, Tang D Y, Zhao X Y, Zhu Y H, Lin J Z, Liu X M.2018. LRRK1, a receptor-like cytoplasmic kinase, regulates leaf rolling through modulating bulliform cell development in rice. Mol Breeding, 38(5): 48. |
| [93] | Zou H Y, Wenwen Y H, Zang G C, Kang Z H, Zhang Z Y, Huang J L, Wang G X.2015. OsEXPB2, a β-expansin gene, is involved in rice root system architecture. Mol Breeding, 35(1): 41. |
| [94] | Zou L P, Sun X H, Zhang Z G, Liu P, Wu J X, Tian C J, Qiu J L, Lu T G.2011. Leaf rolling controlled by the homeodomain leucine zipper class IV gene Roc5 in rice. Plant Physiol, 156(3): 1589-1602. |
| [1] | Prathap V, Suresh KUMAR, Nand Lal MEENA, Chirag MAHESHWARI, Monika DALAL, Aruna TYAGI. Phosphorus Starvation Tolerance in Rice Through a Combined Physiological, Biochemical and Proteome Analysis [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 8-. |
| [2] | Serena REGGI, Elisabetta ONELLI, Alessandra MOSCATELLI, Nadia STROPPA, Matteo Dell’ANNO, Kiril PERFANOV, Luciana ROSSI. Seed-Specific Expression of Apolipoprotein A-IMilano Dimer in Rice Engineered Lines [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 6-. |
| [3] | Sundus ZAFAR, XU Jianlong. Recent Advances to Enhance Nutritional Quality of Rice [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 4-. |
| [4] | Kankunlanach KHAMPUANG, Nanthana CHAIWONG, Atilla YAZICI, Baris DEMIRER, Ismail CAKMAK, Chanakan PROM-U-THAI. Effect of Sulfur Fertilization on Productivity and Grain Zinc Yield of Rice Grown under Low and Adequate Soil Zinc Applications [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 9-. |
| [5] | FAN Fengfeng, CAI Meng, LUO Xiong, LIU Manman, YUAN Huanran, CHENG Mingxing, Ayaz AHMAD, LI Nengwu, LI Shaoqing. Novel QTLs from Wild Rice Oryza longistaminata Confer Rice Strong Tolerance to High Temperature at Seedling Stage [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 14-. |
| [6] | LIN Shaodan, YAO Yue, LI Jiayi, LI Xiaobin, MA Jie, WENG Haiyong, CHENG Zuxin, YE Dapeng. Application of UAV-Based Imaging and Deep Learning in Assessment of Rice Blast Resistance [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 10-. |
| [7] | Md. Forshed DEWAN, Md. AHIDUZZAMAN, Md. Nahidul ISLAM, Habibul Bari SHOZIB. Potential Benefits of Bioactive Compounds of Traditional Rice Grown in South and South-East Asia: A Review [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 5-. |
| [8] | Raja CHAKRABORTY, Pratap KALITA, Saikat SEN. Phenolic Profile, Antioxidant, Antihyperlipidemic and Cardiac Risk Preventive Effect of Chakhao Poireiton (A Pigmented Black Rice) in High-Fat High-Sugar induced Rats [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 11-. |
| [9] | LI Qianlong, FENG Qi, WANG Heqin, KANG Yunhai, ZHANG Conghe, DU Ming, ZHANG Yunhu, WANG Hui, CHEN Jinjie, HAN Bin, FANG Yu, WANG Ahong. Genome-Wide Dissection of Quan 9311A Breeding Process and Application Advantages [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 7-. |
| [10] | JI Dongling, XIAO Wenhui, SUN Zhiwei, LIU Lijun, GU Junfei, ZHANG Hao, Tom Matthew HARRISON, LIU Ke, WANG Zhiqin, WANG Weilu, YANG Jianchang. Translocation and Distribution of Carbon-Nitrogen in Relation to Rice Yield and Grain Quality as Affected by High Temperature at Early Panicle Initiation Stage [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 12-. |
| [11] | Nazaratul Ashifa Abdullah Salim, Norlida Mat Daud, Julieta Griboff, Abdul Rahim Harun. Elemental Assessments in Paddy Soil for Geographical Traceability of Rice from Peninsular Malaysia [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(5): 486-498. |
| [12] | Monica Ruffini Castiglione, Stefania Bottega, Carlo Sorce, Carmelina SpanÒ. Effects of Zinc Oxide Particles with Different Sizes on Root Development in Oryza sativa [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(5): 449-458. |
| [13] | Tan Jingyi, Zhang Xiaobo, Shang Huihui, Li Panpan, Wang Zhonghao, Liao Xinwei, Xu Xia, Yang Shihua, Gong Junyi, Wu Jianli. ORYZA SATIVA SPOTTED-LEAF 41 (OsSPL41) Negatively Regulates Plant Immunity in Rice [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(5): 426-436. |
| [14] | Ammara Latif, Sun Ying, Pu Cuixia, Noman Ali. Rice Curled Its Leaves Either Adaxially or Abaxially to Combat Drought Stress [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(5): 405-416. |
| [15] | Liu Qiao, Qiu Linlin, Hua Yangguang, Li Jing, Pang Bo, Zhai Yufeng, Wang Dekai. LHD3 Encoding a J-Domain Protein Controls Heading Date in Rice [J]. Rice Science, 2023, 30(5): 437-448. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||